As part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA or health care reform law), starting in 2014 ALL Americans must have a minimum amount of health insurance or be taxed by the government. The law also requires each state to have a health insurance exchange
Exchange = a new place to shop for and buy health insurancewhere people can buy health insurance coverage. People who don't get health insurance at work, or can't afford it, may be able to get it through an exchange. The exchange do not replace buying health insurance privately. They are simply a new place to shop and buy.

On the exchange, individuals and small businesses can buy qualified health plans (QHPs). Exchanges can be set up in one of three ways. Each state determines how its exchange will be set up:
Exchange plans will be offered in a tiered format. The tiers are named after metals: bronze, silver, gold and platinum. Each tier will have several plans to choose from and will include essential health benefits.
Exchange plans are tiered:Bronze plans will have the lowest monthly premium, but cost shares will be more when health care services are provided. Platinum plans will have the highest monthly premium, but cost shares will be less.
- Platinum - 90% coverage
- Gold - 80% coverge
- Silver - 70% coverage
- Bronze - 60% coverage
All plans must include "essential health benefits" as defined by the health care reform law. Specifically, the plans must include items and services from at least these 10 categories of care.*
All health plans must follow new coverage and benefit rules starting in 2014 (see the chart below and read on for details about exchange coverage and essential health benefits). These requirements are based on:
Premiums for these individual and small group plans will not be based on health status. Instead, they will be based on family tier, age, geography and tobacco use. (State-specific rules may vary when a federally run model is not in place.) These plans also must use "3 to 1" age bands. This mans the highest preimum cannot be more than three times the lowest premium for the same plan. All of these requirements may have an impact on rates, although the specific effects are difficult to define at this time as qualified health plans continue to be developed
| Inside exchange | Outside exchange - fully insured small group and individual | Outside exchange - fully insured large group and self-insured | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Include essential health benefits | |||
| Provide 60% actuarial value minimum | |||
| Adhere to deductible and out-of-pocket maximum limits | |||
| Comply with "metal levels" - benefit tiers with specific actuarial values (60% 70% 80% 90%) | |||
| Be certified by the exchange through wich the plan is offered (certification requirement to be determined) |
*The helath care reform law does not require carriers to offer plans with at least a 60% actuarial value, nor does it require employers to provide health coverage. However, it imposes penalties on 50+ employers that do not provide minimum coverage.
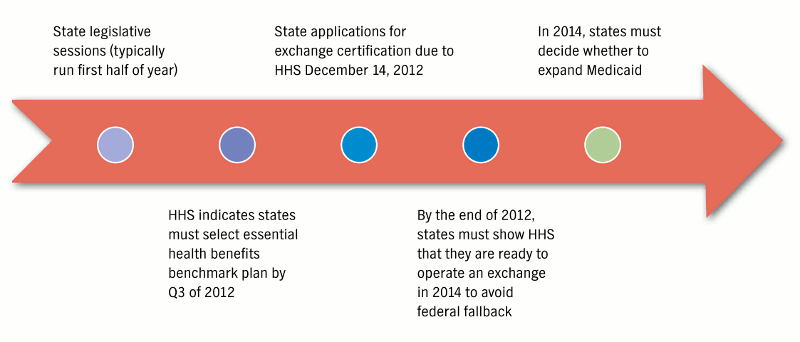
If all goes as planned, exchanges will open for enrollment on October 1, 2013. Coverage effective dates will begin January 1, 2014. And in 2017, states have the option to offer plans on the exchanges to large group employers with 100 or more employees.